What are Lab Diamonds?
Lab diamonds are real diamonds that are created in a laboratory rather than being mined from the earth. Chemically, physically, and optically, they are identical to mined diamonds—they’re both made of pure carbon arranged in a crystal lattice.
Here are some key points about them:
- Creation methods: Lab diamonds are grown using advanced technology that mimics the natural conditions under which diamonds form in the earth. The two main processes are:
- HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) – replicates the heat and pressure found deep underground.
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) – grows diamonds layer by layer from a carbon-rich gas.
- Appearance: They look the same as mined diamonds and require professional equipment to distinguish. Even trained gemologists usually can’t tell the difference with the naked eye.
- Cost: Lab diamonds are generally 30–50% less expensive than comparable natural diamonds, making them a more affordable option.
- Ethics and environment: Many people choose lab-grown diamonds because they avoid the environmental disruption and ethical concerns sometimes linked to traditional diamond mining.
- Certification: Like natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds are certified by independent gem labs (like GIA or IGI) for their cut, color, clarity, and carat weight.
What are the 4Cs?
Lab diamonds are graded just as critically as mined diamonds. But just what do the 4Cs mean when it comes to grading?
Color
One of the most important aspects of a diamond is its color. Designations of color run from D through Z, and are grouped by the amount of yellow is present.
When the diamond contains enough yellow, it then becomes a Fancy Yellow and its value begins to increase depending on the saturation level as well as how it rates in the other Cs.
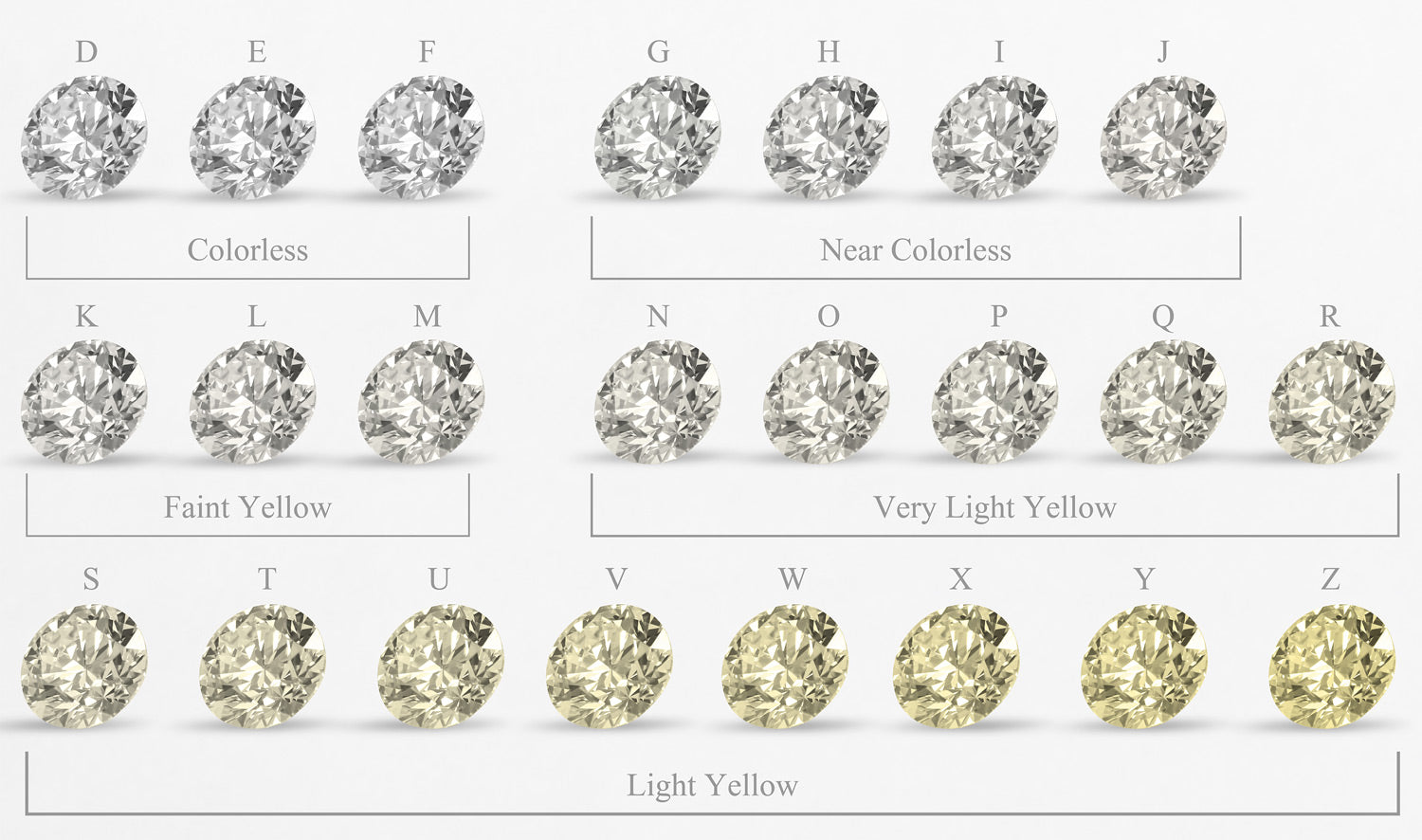

- DEF - Colorless. This is the highest grade for diamonds and contains no yellow at all.
- GHIJ - Near Colorless. A very small amount of yellow is found.
- KLM - Faint Yellow
- N - R - Very Light Yellow
- S - Z - Light Yellow
Clarity
Clarity is very important when it comes to diamonds, even more so than other gems. Clarity refers to the size, amount, and location of inclusions within the diamond, as well as their visibility. The most common inclusions found would be carbon. These can range from miniscule black flecks to large chunks.
Clarity grading is done with 10x magnification:
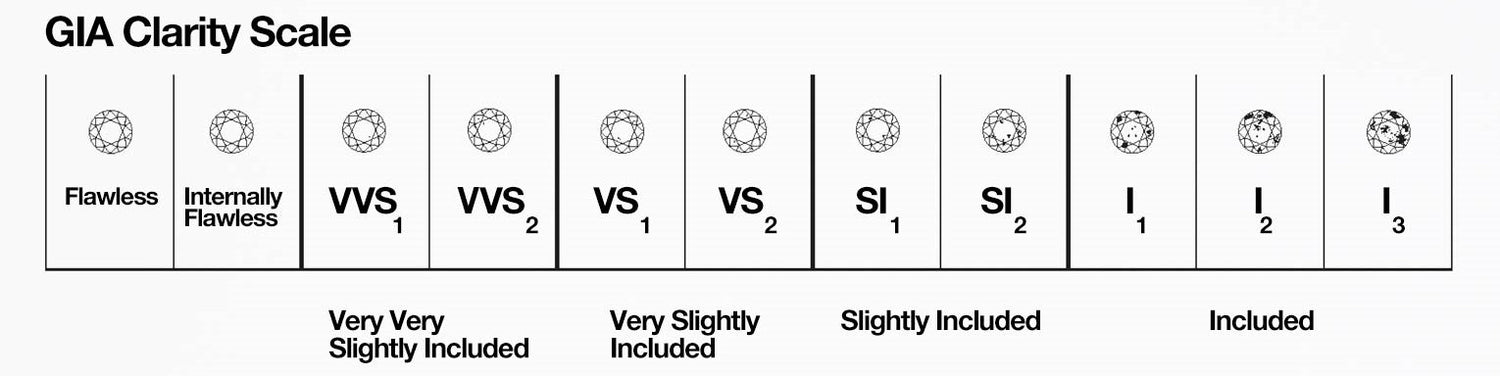
- FL (Flawless) - No inclusions or blemishes
- IF (Internally Flawless) - No inclusions but has insignificant blemishes
- VVS1 & VVS2 (Very Very Slightly Included) - Minute inclusions from extremely difficult to see (VVS1), to very difficult to see (VVS2)
- VS1 & VS2 (Very Slightly Included) - Minor inclusions that range from difficult (VS1) to somewhat easy to see (VS2)
- SI1 & SI2 (Slightly Included) - Noticeable inclusions that are easy (SI1) or very easy to see (SI2)
- I1, I2, & I3 (Included) - Obvious inclusions
- Salt & Pepper - These diamonds don’t qualify for the same grading as white diamonds as their inclusions are part of their unique appeal
Carat & Cut
We all know how important carat weight is, but it’s important to keep in mind the quality of the cut too.
Diamond carat weights are recorded to the hundredth of a decimal. It’s so accurate, that the carat weight can change vastly due to the difference in the thickness of the girdle.
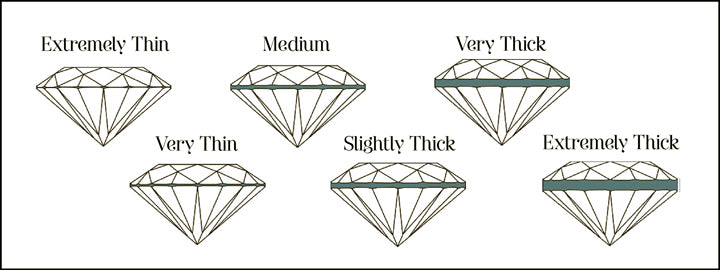
For example, two diamonds can have the same diameter, but the diamond with a thicker girdle will weigh more.
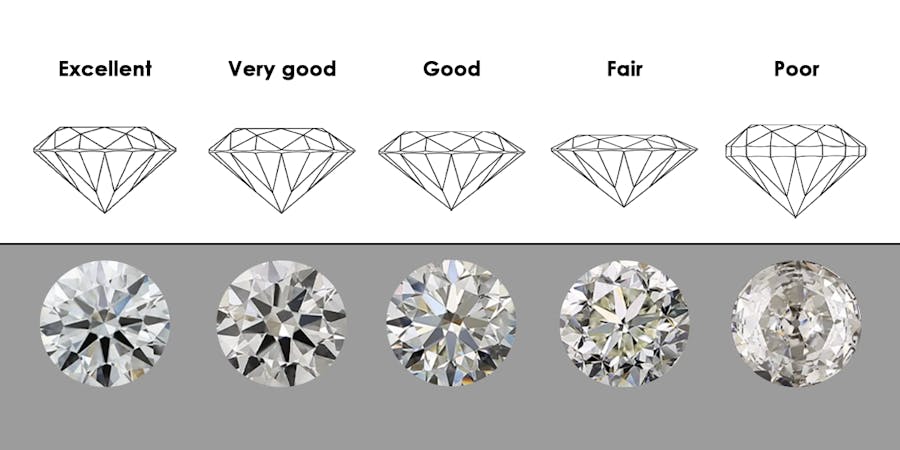

The quality of the cut doesn’t just affect the carat weight, it also affects the reflection pattern of the diamond. A well cut diamond will show its stunning brilliance without windowing or extinction zones.
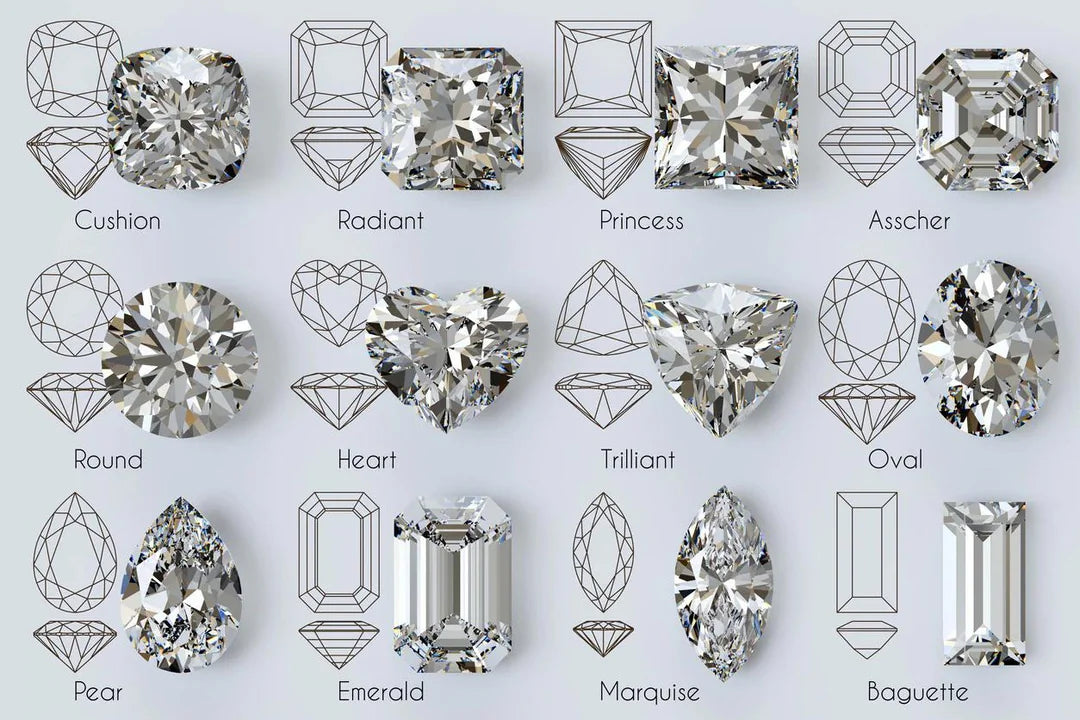

Diamonds are offered in many different shapes and cuts, each with their own beauty.
Choosing the perfect diamond for you is a matter of personal preference and which of the 4Cs is most important to you.
We would love to help you find your perfect diamond!
Contact Us to begin your search today.